Workload Federation with AWS and Terraform Cloud
Workload Federation with AWS and Terraform Cloud
Here we are going to cover connecting an AWS Role with a Terraform Cloud workspace. This is a common pattern for managing without needing to store long-lived credentials in your Terraform code. This greatly reduce the chances of high-privilege credentials being exposed.
Prerequisites
A few things you’ll need to have in place before you get started:
- An AWS account with permissions to create IAM roles and policies
- A Terraform Cloud account
- The Terraform CLI installed on your local machine
Step 1: Set the credentials in Terraform Cloud for the role with access to AWS
- Log in to your Terraform Cloud account.
- Create a new Workspace for this AWS account.
- In the wWorkspace, go to the Variables tab.
- Set the following sensitive environment variables how to get access credential (Ensure that the AWS account has the necessary permissions to create IAM roles and policies)
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRETAWS_SESSION_TOKEN- (optional)
- Set the following non-sensitive environment variables (this is to keep information out of the code):
project- The name of the project in Terraform Cloudorganization- The name of the organization in Terraform Cloudworkspace- The name of the workspace in Terraform Cloudaudience- The audience for the OpenID Connect Provider
- Save The variables.
- Create a new Private GitHub repository and connect it to the workspace.
Step 2: Create the Terraform configuration
- Clone the repository to your local machine.
- Add a new Terraform configuration file,
main.tf.Add the following code to the file to create an IAM role, Identify provider, and trust relationship in AWS:
terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "~> 5.0" } tls = { source = "hashicorp/tls" version = "4.0.5" } } } variable "workspace" { type = string description = "Terraform Cloud Workspace to be granted access to AWS" } variable "organization" { type = string description = "Terraform Cloud Organization to be granted access" } variable "project" { type = string description = "Terraform Cloud Project to be granted access" } variable "audience" { type = string default = "aws.workload.identity" description = "The audience to be configured for AWS to be looking for" } provider "aws" { region = "us-east-1" } ### Getting the certificate information for Terraform cloud endpoint data "tls_certificate" "app_terraform" { url = "https://app.terraform.io" } ### Registering the Identity provider of Terraform Cloud with the audience above resource "aws_iam_openid_connect_provider" "oidc" { url = "https://app.terraform.io" client_id_list = [var.audience] thumbprint_list = [data.tls_certificate.app_terraform.certificates[0].sha1_fingerprint] } # Creating Policy to allow the workspace to assume the role. # The format of the Sub is defined here https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/cloud-docs/workspaces/dynamic-provider-credentials/workload-identity-tokens#token-specification data "aws_iam_policy_document" "assume_role_policy" { statement { actions = ["sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity"] effect = "Allow" condition { test = "StringLike" variable = "${replace(aws_iam_openid_connect_provider.oidc.url, "https://", "")}:sub" # This creates a mapping to the workspace based on an Exact match organization,project,workspace. values = ["organization:${var.organization}:project:${var.project}:workspace:${var.workspace}:run_phase:*"] } principals { identifiers = [aws_iam_openid_connect_provider.oidc.arn] type = "Federated" } } } # Create the role for Terraform to use, in this case we are giving admin as we want it to create IAM permissions # You should create narrower roles for less privileged workspaces. resource "aws_iam_role" "tfc_role" { assume_role_policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume_role_policy.json name = "TFC-Admin" managed_policy_arns = ["arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess"] force_detach_policies = true } # Output the Role ARN so that it can be read to be used in Workload Federation. output "role_arn" { value = aws_iam_role.tfc_role.arn description = "Role created that Terraform Cloud can assume with STS" }
- You can now commit the code to your repository and trigger a run in Terraform Cloud.
- You should see the following plan in the Terraform Cloud UI. It should just be 2 resources to create, and 2 datasource’s to read.
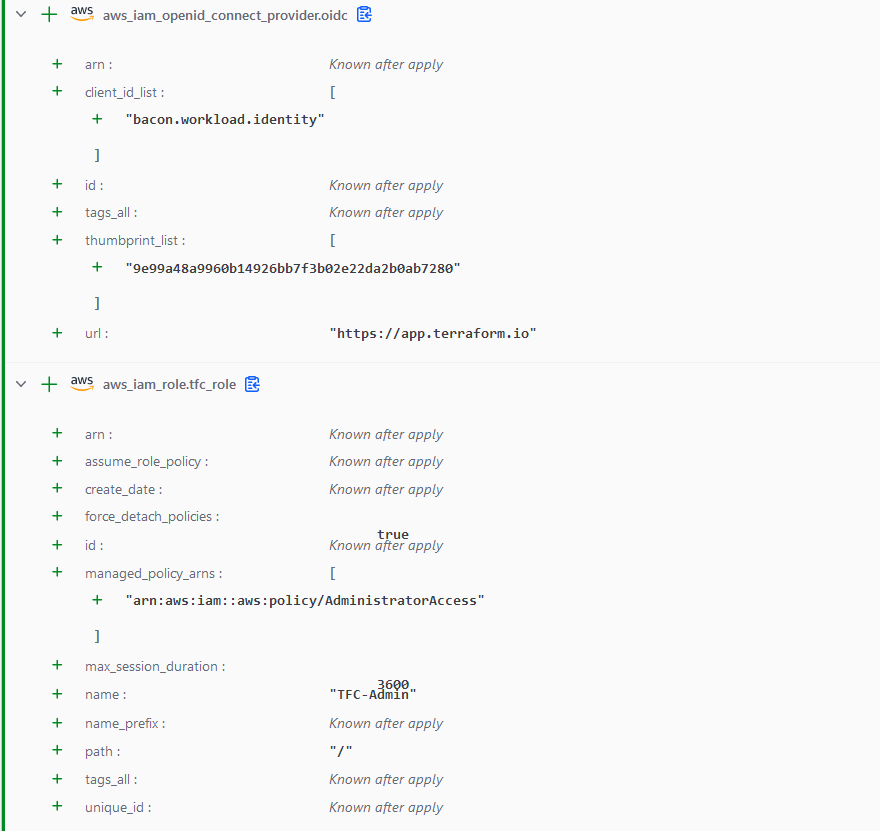
- Apply the plan to create the resources in AWS.
- Once the run is complete, make note of the ARN of the role that was created. You will need this in the next step.
Step 3: Configure the Terraform Cloud workspace to use Dynamic Provider Configuration
- In the Terraform Cloud workspace, go to the variables tab.
- Delete following variables:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDAWS_SECRETAWS_SESSION_TOKEN
- Add the following environment variables:
TFC_AWS_RUN_ROLE_ARN- The ARN of the role you created in AWS, it Should be in Output of the Terraform run before.TFC_AWS_WORKLOAD_IDENTITY_AUDIENCE- The audience for the OpenID Connect Provider, this should be the same as the audience you set in the Terraform Cloud workspace.TFC_AWS_PROVIDER_AUTH- This should be set to true.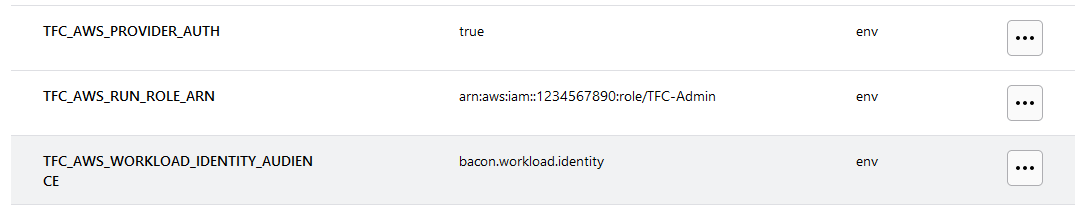
- Save the variables.
- Trigger a new run in Terraform Cloud.
- You should see no changes, and the run should complete successfully.
Step 4: Congratulations! You have successfully connected an AWS Role with a Terraform Cloud workspace.
Now you can use this role to manage resources in AWS without needing to store long-lived credentials in your Terraform code, you can now add mappings to new roles and workspace to manage different resources in AWS, and to allow other teams access to resources in AWS. The creation of the OIDC provider should only need to be done once per AWS account, and the roles can be created as needed.